![[INTEL NAVIGATION HEADER]](../../PIX/HEADER.GIF)
Intel's 2.7V SmartVoltage Flash Memory Advances Low-Power High-Performance Mobile Applications
Mobile applications strive for longer battery life combined with the right system features.
This need for longer battery life drives system voltage lower. In contrast, the right system features often drive
performance requirements higher. Intel's SmartVoltage technology advances Intel's leading NOR flash
memory solutions to satisfy these requirements with the lowest voltage and highest performance solution
at 2.7V and 120 ns. Available in upgradable 4- and 8-Mbit product families, these extended-temperature
2.7V SmartVoltage products set the pace for future trends in mobile applications.

Mobile Applications Drive the Need for Low Voltage and High Performance
Cellular phone users desire longer talk-time. Users, as well as
cellular service providers, demand longer standby time when their phone is waiting to receive an
incoming call. While research continues for a more cost-effective battery with longer life, today's clear
directive is to lower the system voltage. Lowering the voltage from 5V to 2.7V more than doubles the
battery life. In cellular phones, this translates to twice the talk time and four times the standby time. This
improvement comes from discharging the battery to the lower voltage and reducing overall system power consumption at 2.7V.
While lowering voltage extends precious battery life, it also reduces the current supplied to system
components. Traditionally, this runs counter to maintaining performance. At the same time,
high-performance remains critical since mobile applications execute all facets of operation directly out of
high performance flash memory. Therefore, the right solution must meet both the voltage and
performance requirements of the application.
Intel's 2.7V, 120 ns SmartVoltage Boot Block Products Advance Mobile Applications
Intel's new 2.7V, 4- and 8-Mbit SmartVoltage boot block flash memories, manufactured on Intel's
advanced 0.6 µ ETOX(TM) IV flash technology, lead the way in low-voltage read operation and high
performance. The figure below provides a comparison of performance and voltage for 4-Mbit memory
products from several manufacturers.
Comparison of 4-Mbit Flash Memory Products
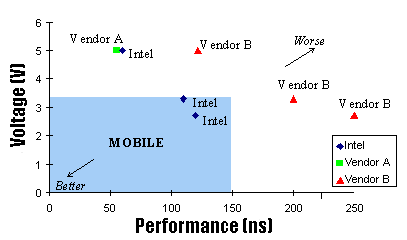

Mobile Applications Require Low Voltage and High Performance
Mobile applications are represented by the shaded area in the
lower left of the figure, bounded by 3.3V maximum voltage and 150 ns maximum performance. To use a
memory outside these boundaries requires significant tradeoffs in battery life or the right system features.
Intel Leads in Low-Voltage Flash Memory
Intel has been developing low-voltage design techniques since its first 3.3V products, introduced in 1992.
Intel's SmartVoltage technology incorporates three fundamental advances to enable 2.7V capability:
- Address Transition Detection applies a circuit technique used for many
years on high-speed SRAM to flash memory. On-chip circuitry detects address and control input
transitions. An internal control pipe pre-charges read circuits ahead of address decoding logic. This
speeds up array access once the complete address is decoded. This patented flash memory approach, first
applied to Intel's high-volume boot block family at 5V, provides significant performance benefits when
optimized for low-voltage operation.
- Low-Voltage Margin Sensing increases performance while maintaining
proper noise margins during array sensing. By increasing the array cell current, a greater differential is
achieved during sensing which provides faster operation and greater noise margin.
- Output Auto-detect circuitry determines optimal output drive
characteristics for low voltage. This ensures high-speed switching while optimizing the supply current
profile for optimal noise characteristics.
Building on Intel's Widely Adopted SmartVoltage Products
These 2.7V advancements build on the key attributes that make Intel's SmartVoltage technology the
leading solution today for mobile applications. Intel's complete family of 2-, 4-, and 8-Mbit SmartVoltage
boot block products deliver:
- High speed parallel random access for direct code execution: Today's
applications use flash memory predominantly for direct code execution. This requires that any random
access to memory provide sustained high-performance, parallel access. Intel's NOR architecture provides
parallel access for both x8 and x16 operation. Anything less, such as slow initial access featured on
alternative architectures, will not meet the performance requirements of the application.
- Low-voltage read using two supply pins for flexible, cost-effective
solutions, including single-supply. By using two separate supply pins, SmartVoltage allows the read
supply to be driven lower than the write/erase voltage. As a result, SmartVoltage delivers a cost-effective,
low-voltage solution on a given technology sooner than a single supply-approach. As technology
advances to allow cost-effective, low-voltage write and erase, this capability is easily integrated into
SmartVoltage.
- 12V High-speed programming for fast production throughput: High-speed
programming has proven to be invaluable for high-volume manufacturing, doubling production
throughput. During the production process, high-volume manufacturers apply a readily available 12V
supply to their system board using industry-standard production equipment. Accelerated write and erase
times at 12V speed production throughput, thereby saving tester-equipment costs and improving
time-to-market.
- Optimal 5V in-system writes for updating the memory in-system:
SmartVoltage also allows for the simplicity of 5V in-system reads and writes. For 5V applications the
write/erase voltage (VPP) is simply shorted to the read voltage (VCC). On-chip circuitry automatically
senses the write/erase voltage applied to the memory and implements internal write and erase operations.
Dedicated control of the write/erase supply also provides absolute write protection by grounding the
supply during normal read operation.
- Automatic Power Savings (APS) for longer system battery life: APS mode
reduces active current by automatically shutting down inactive circuits when the memory is not being
accessed. This proves to be a key feature for further reducing system power consumption.
Conclusion
Mobile applications, such as cellular phones, are trending to lower voltages while maintaining their
performance requirements. Intel's SmartVoltage technology advances Intel's leading NOR flash memory
products to deliver the optimal solutions. Architectural advancements enable the lowest voltage, highest
performance solution today with 120ns performance at 2.7V extended-temperature operation. This new
capability builds on the key attributes that make Intel's SmartVoltage technology the right choice for
mobile applications. Intel's SmartVoltage technology sets the pace for future trends to subsequent lower
voltage and higher performance.
Legal Stuff © 1997 Intel Corporation